Embedded images
Muscat supports the upload of single embedded images. These are useful for enhancing the cataloguing work with, for example, hand-writing or watermark illustrations. Images are directly stored on the server. They can be linked to various resources in a many-to-many way. This means that an image can be linked to both a personal name (e.g., the composer or copyist) and to a source (e.g., the manuscript description from which the image was taken).
Embedded images simply have to be uploaded from the Muscat cataloguing interface. A short description of the image must be added. Links to other resources can be added to the image where appropriate.
IIIF support
In addition to embedded images, Muscat also supports the International Image Interoperability Framework (IIIF). This means that images published by libraries or archives through this protocol can be displayed directly within the discovery interface of Muscat. The images do not need to be uploaded and hosted on the Muscat server but are instead accessed dynamically directly from the original hosting institution. The display of IIIF images in Muscat is powered by Diva.js, a high resolution open-source image viewer developed by the DDMAL at McGill University.
See a live example of the display of the complete set of high-resolution images for a source served via IIIF on the RISM Switzerland installation of Muscat.
One interesting feature of this architecture is that it makes it possible to gather images in one place. For prints, where in many cases multiple copies exist, this means they can be viewed directly within Muscat while held physically in libraries located around the world, and their images served from independent servers.
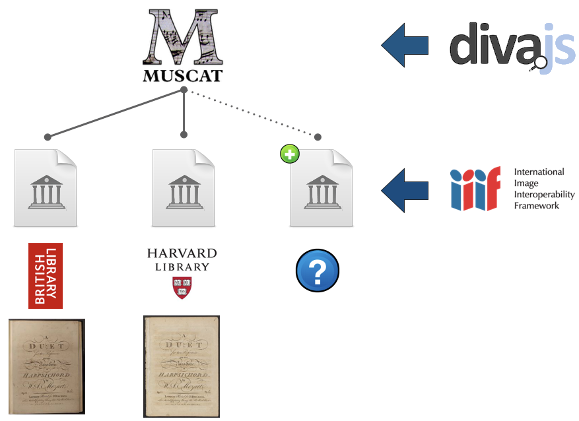
Diva.js is fully integrated into the Muscat discovery interface and the images are displayed within the source description. It is also possible to open it in full-screen mode and to adjust the zoom level as desired.